QoS¶
This section describes how to use QoS functions that can be set using REST.
About QoS¶
QoS (Quality of Service) is a technology that can transfer the data in accordance with the priority based on the type of data, and reserve network bandwidth for a particular communication in order to communicate with a constant communication bandwidth on the network.
Example of the operation of the per-flow QoS¶
The following shows an example of creating topology, adding Queue settings and rules to reserve network bandwidth. And this example shows traffic shaping at WAN side interface of OFS1.
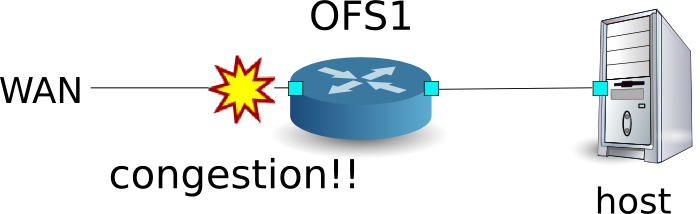
Building the environment¶
First, build an environment on Mininet. Parameters of the mn command are as
follows.
| Parameters | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| mac | None | Set the MAC address of the host automatically |
| switch | ovsk | Use Open vSwitch |
| controller | remote | Use an external one for OpenFlow controller |
| x | None | Start xterm |
An execution example is as follows.
$ sudo mn --mac --switch ovsk --controller remote -x
*** Creating network
*** Adding controller
Unable to contact the remote controller at 127.0.0.1:6633
*** Adding hosts:
h1 h2
*** Adding switches:
s1
*** Adding links:
(h1, s1) (h2, s1)
*** Configuring hosts
h1 h2
*** Running terms on localhost:10.0
*** Starting controller
*** Starting 1 switches
s1
*** Starting CLI:
mininet>
Also, start another xterm for the controller.
mininet> xterm c0
mininet>
Next, set the version of OpenFlow to be used in each router to version 1.3 and set to listen on port 6632 to access OVSDB.
switch: s1 (root):
# ovs-vsctl set Bridge s1 protocols=OpenFlow13
# ovs-vsctl set-manager ptcp:6632
Then, modify simple_switch_13.py used in “Switching Hub”. rest_qos.py suppose to be processed on Flow Table pipeline processing, modify simple_switch_13.py to register flow entry into table id:1.
controller: c0 (root)
# sed '/OFPFlowMod(/,/)/s/)/, table_id=1)/' ryu/ryu/app/simple_switch_13.py > ryu/ryu/app/qos_simple_switch_13.py
# cd ryu/; python ./setup.py install
Finally, start rest_qos, qos_simple_switch_13 and rest_conf_switch on xterm of controller.
controller: c0 (root):
# ryu-manager ryu.app.rest_qos ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13 ryu.app.rest_conf_switch
loading app ryu.app.rest_qos
loading app ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13
loading app ryu.app.rest_conf_switch
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
instantiating app None of DPSet
creating context dpset
instantiating app None of ConfSwitchSet
creating context conf_switch
creating context wsgi
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_conf_switch of ConfSwitchAPI
instantiating app ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13 of SimpleSwitch13
instantiating app ryu.controller.ofp_handler of OFPHandler
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_qos of RestQoSAPI
(3519) wsgi starting up on http://0.0.0.0:8080/
After a successful connection between the router and Ryu, the following message appears.
controller: c0 (root):
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000001: Join qos switch.
If the above log is displayed for the three routers, preparation is complete.
Queue Setting¶
Set the Queue to switch.
| Queue ID | Max rate | Min rate |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 500Kbps | - |
| 1 | (1Mbps) | 800Kbps |
Note
For details of REST API used in the following description, see “REST API List” at the end of the section.
First, set ovsdb_addr in order to access OVSDB.
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X PUT -d '"tcp:127.0.0.1:6632"' http://localhost:8080/v1.0/conf/switches/0000000000000001/ovsdb_addr
#
Also, execute setting of Queue.
# curl -X POST -d '{"port_name": "s1-eth1", "type": "linux-htb", "max_rate": "1000000", "queues": [{"max_rate": "500000"}, {"min_rate": "800000"}]}' http://localhost:8080/qos/queue/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": {
"result": "success",
"details": {
"0": {
"config": {
"max-rate": "500000"
}
},
"1": {
"config": {
"min-rate": "800000"
}
}
}
}
}
]
Note
The result of the REST command is formatted for easy viewing.
QoS Setting¶
Install the following flow entry to the switch.
| (Priority) | Destination address | Destination port | Protocol | Queue ID | (QoS ID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.0.0.1 | 5002 | UDP | 1 | 1 |
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"nw_dst": "10.0.0.1", "nw_proto": "UDP", "tp_dst": "5002"}, "actions":{"queue": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
Verifying the Setting¶
Check the contents of the setting of the switch.
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"nw_proto": "UDP",
"tp_dst": 5002,
"qos_id": 1,
"nw_dst": "10.0.0.1",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "1"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
]
Measuring the bandwidth¶
Try to measure the bandwidth by using iperf. In the following example, h1(server) listens on the port 5001 and 5002 with UDP protocol. h2(client) sends 1Mbps UDP traffic to the port 5001 on h1 and 1Mbps UDP traffic to the port 5002 on h1
Note
The fallowing examples use iperf (http://iperf.fr/) to measure the bandwidth. But this document does not describe how to install iperf and how to use it.
First, start another xterm on each h1 and h2.
mininet> xterm h1
mininet> xterm h2
Node: h1(1) (root):
# iperf -s -u -i 1 -p 5001
...
Node: h1(2) (root):
# iperf -s -u -i 1 -p 5002
...
Node: h2(1) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5001 -u -b 1M
...
Node: h2(2) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5002 -u -b 1M
...
Node: h1(1) (root):
[ 4] local 10.0.0.1 port 5001 connected with 10.0.0.2 port 50375
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 4] 0.0- 1.0 sec 60.3 KBytes 494 Kbits/sec 12.208 ms 4/ 42 (9.5%)
[ 4] 0.0- 1.0 sec 4 datagrams received out-of-order
[ 4] 1.0- 2.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.538 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 2.0- 3.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.494 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 3.0- 4.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.625 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 4.0- 5.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.576 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 5.0- 6.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.561 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 6.0- 7.0 sec 11.5 KBytes 94.1 Kbits/sec 45.536 ms 0/ 8 (0%)
[ 4] 7.0- 8.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 92.790 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 8.0- 9.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 135.391 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 9.0-10.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 167.045 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 10.0-11.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 193.006 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 11.0-12.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 213.944 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 12.0-13.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 231.981 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 13.0-14.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 249.758 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 14.0-15.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 261.139 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 15.0-16.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 269.879 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 16.0-17.0 sec 12.9 KBytes 106 Kbits/sec 204.755 ms 0/ 9 (0%)
[ 4] 17.0-18.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 26.214 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 18.0-19.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 13.485 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 19.0-20.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.690 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 20.0-21.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.498 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 21.0-22.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.601 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 22.0-23.0 sec 60.3 KBytes 494 Kbits/sec 12.640 ms 0/ 42 (0%)
[ 4] 23.0-24.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.508 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 24.0-25.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.578 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 25.0-26.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.541 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 26.0-27.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.539 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 27.0-28.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.578 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 28.0-29.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.527 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 29.0-30.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.542 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 0.0-30.6 sec 1.19 MBytes 327 Kbits/sec 12.562 ms 4/ 852 (0.47%)
[ 4] 0.0-30.6 sec 4 datagrams received out-of-order
Node: h1(2) (root):
[ 4] local 10.0.0.1 port 5002 connected with 10.0.0.2 port 60868
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 4] 0.0- 1.0 sec 112 KBytes 917 Kbits/sec 4.288 ms 0/ 78 (0%)
[ 4] 1.0- 2.0 sec 115 KBytes 941 Kbits/sec 4.168 ms 0/ 80 (0%)
[ 4] 2.0- 3.0 sec 115 KBytes 941 Kbits/sec 4.454 ms 0/ 80 (0%)
[ 4] 3.0- 4.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.226 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 4.0- 5.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.096 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 5.0- 6.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.225 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 6.0- 7.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.055 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 7.0- 8.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.241 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 8.0- 9.0 sec 115 KBytes 941 Kbits/sec 3.886 ms 0/ 80 (0%)
[ 4] 9.0-10.0 sec 112 KBytes 917 Kbits/sec 3.969 ms 0/ 78 (0%)
[ 4] 0.0-10.8 sec 1.19 MBytes 931 Kbits/sec 4.287 ms 0/ 852 (0%)
The above result shows the traffic sent to the port 5001 is shaped with up to 500Kbps and the traffic to the port 5002 is guaranteed 800Kbps bandwidth.
Example of the operation of QoS by using DiffServ¶
Previous example shows the per-flow QoS, while it is able to control finely, as the communication flows increase, the flow entries which are set for each switch to control the bandwidth also increase. So the per-flow QoS is not scalable. Therefore, the following example divides flows into the several QoS classes at the entrance router of DiffServ domain and applies DiffServ to control flows for each class. DiffServ forward the packets according to PHB defined by DSCP value which is the first 6-bit of ToS field in IP header, and realizes QoS.
The following shows an example of setting Queue and bandwidth configuration based on the QoS class into Switch (Router) OFS1, and installation rules of marking the DSCP value in accordance with the flow. And this example shows traffic shaping at WAN side interface of OFS1.

Building the environment¶
First, build an environment on Mininet. Parameters of the mn command are as
follows.
| Parameters | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| topo | linear,2 | Topology where two switches are connected serially |
| mac | None | Set the MAC address of the host automatically |
| switch | ovsk | Use Open vSwitch |
| controller | remote | Use an external one for OpenFlow controller |
| x | None | Start xterm |
An execution example is as follows.
$ sudo mn --topo linear,2 --mac --switch ovsk --controller remote -x
*** Creating network
*** Adding controller
Unable to contact the remote controller at 127.0.0.1:6633
*** Adding hosts:
h1 h2
*** Adding switches:
s1
*** Adding links:
(h1, s1) (h2, s1)
*** Configuring hosts
h1 h2
*** Running terms on localhost:10.0
*** Starting controller
*** Starting 1 switches
s1
*** Starting CLI:
mininet>
Also, start another xterm for the controller.
mininet> xterm c0
mininet>
Next, set the version of OpenFlow to be used in each router to version 1.3 and set to listen on port 6632 to access OVSDB.
switch: s1 (root):
# ovs-vsctl set Bridge s1 protocols=OpenFlow13
# ovs-vsctl set-manager ptcp:6632
switch: s2 (root):
# ovs-vsctl set Bridge s2 protocols=OpenFlow13
Then, delete the IP address that is assigned automatically on each host and set a new IP address.
host: h1:
# ip addr del 10.0.0.1/8 dev h1-eth0
# ip addr add 172.16.20.10/24 dev h1-eth0
host: h2:
# ip addr del 10.0.0.2/8 dev h2-eth0
# ip addr add 172.16.10.10/24 dev h2-eth0
And, modify rest_router.py used in “Router”. rest_qos.py suppose to be processed on Flow Table pipeline processing, modify rest_router.py to register flow entry into table id:1.
controller: c0 (root):
# sed '/OFPFlowMod(/,/)/s/0, cmd/1, cmd/' ryu/ryu/app/rest_router.py > ryu/ryu/app/qos_rest_router.py
# cd ryu/; python ./setup.py install
Finally, start rest_qos, qos_rest_router and rest_conf_switch on xterm of controller.
controller: c0 (root):
# ryu-manager ryu.app.rest_qos ryu.app.qos_rest_router ryu.app.rest_conf_switch
loading app ryu.app.rest_qos
loading app ryu.app.qos_rest_router
loading app ryu.app.rest_conf_switch
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
instantiating app None of DPSet
creating context dpset
instantiating app None of ConfSwitchSet
creating context conf_switch
creating context wsgi
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_conf_switch of ConfSwitchAPI
instantiating app ryu.app.qos_rest_router of RestRouterAPI
instantiating app ryu.controller.ofp_handler of OFPHandler
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_qos of RestQoSAPI
(4687) wsgi starting up on http://0.0.0.0:8080/
After a successful connection between the router and Ryu, the following message appears.
controller: c0 (root):
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Set SW config for TTL error packet in.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Set ARP handling (packet in) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Set L2 switching (normal) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Set default route (drop) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Start cyclic routing table update.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Join as router.
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000002: Join qos switch.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Set SW config for TTL error packet in.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Set ARP handling (packet in) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Set L2 switching (normal) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Set default route (drop) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Start cyclic routing table update.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Join as router.
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000001: Join qos switch.
If the above log is displayed for the three routers, preparation is complete.
Queue Setting¶
| Queue ID | Max rate | Min rate | Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1Mbps | - | Default |
| 1 | (1Mbps) | 200Kbps | AF3 |
| 2 | (1Mbps) | 500Kbps | AF4 |
Note
For details of REST API used in the following description, see “REST API List” at the end of the section.
First, set ovsdb_addr in order to access OVSDB.
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X PUT -d '"tcp:127.0.0.1:6632"' http://localhost:8080/v1.0/conf/switches/0000000000000001/ovsdb_addr
#
Also, execute setting of Queue.
# curl -X POST -d '{"port_name": "s1-eth1", "type": "linux-htb", "max_rate": "1000000", "queues":[{"max_rate": "1000000"}, {"min_rate": "200000"}, {"min_rate": "500000"}]}' http://localhost:8080/qos/queue/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": {
"result": "success",
"details": {
"0": {
"config": {
"max-rate": "1000000"
}
},
"1": {
"config": {
"min-rate": "200000"
}
},
"2": {
"config": {
"min-rate": "500000"
}
}
}
}
}
]
Note
The result of the REST command is formatted for easy viewing.
Router Setting¶
Set the IP address and the default route for each router.
# curl -X POST -d '{"address": "172.16.20.1/24"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add address [address_id=1]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"address": "172.16.30.10/24"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add address [address_id=2]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"gateway": "172.16.30.1"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add route [route_id=1]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"address": "172.16.10.1/24"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add address [address_id=1]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"address": "172.16.30.1/24"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add address [address_id=2]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"gateway": "172.16.30.10"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add route [route_id=1]"
}
]
}
]
...
The IP address settings for each router are done, register the routers as the default gateway to each host.
host: h1:
# ip route add default via 172.16.20.1
host: h2:
# ip route add default via 172.16.10.1
QoS Setting¶
Install the following flow entry in accordance with DSCP value into the router (s1).
| Priority | DSCP | Queue ID | (QoS ID) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26(AF31) | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 34(AF41) | 2 | 2 |
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "26"}, "actions":{"queue": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "34"}, "actions":{"queue": "2"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=2"
}
]
}
]
Install the following rules of marking the DSCP value into the router (s2).
| (Priority) | Destination address | Destination port | Protocol | DSCP | (QoS ID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 172.16.20.10 | 5002 | UDP | 26(AF31) | 1 |
| 1 | 172.16.20.10 | 5003 | UDP | 34(AF41) | 2 |
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"nw_dst": "172.16.20.10", "nw_proto": "UDP", "tp_dst": "5002"}, "actions":{"mark": "26"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"nw_dst": "172.16.20.10", "nw_proto": "UDP", "tp_dst": "5003"}, "actions":{"mark": "34"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=2"
}
]
}
]
Verifying the Setting¶
Check the contents of the setting of each switch.
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"ip_dscp": 34,
"actions": [
{
"queue": "2"
}
],
"qos_id": 2
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"ip_dscp": 26,
"actions": [
{
"queue": "1"
}
],
"qos_id": 1
}
]
}
]
}
]
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"nw_proto": "UDP",
"tp_dst": 5002,
"qos_id": 1,
"nw_dst": "172.16.20.10",
"actions": [
{
"mark": "26"
}
]
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"nw_proto": "UDP",
"tp_dst": 5003,
"qos_id": 2,
"nw_dst": "172.16.20.10",
"actions": [
{
"mark": "34"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
]
Measuring the bandwidth¶
Try to measure the bandwidth by using iperf. In the following example, h1(server) listens on the port 5001, 5002 and 5003 with UDP protocol. h2(client) sends 1Mbps UDP traffic to the port 5001 on h1, 300Kbps UDP traffic to the port 5002 on h1 and 600Kbps UDP traffic to the port 5003.
First, start 2 xterm on h2.
mininet> xterm h2
mininet> xterm h2
Node: h1(1) (root):
# iperf -s -u -p 5002 &
...
# iperf -s -u -p 5003 &
...
# iperf -s -u -i 1 5001
------------------------------------------------------------
Server listening on UDP port 5001
Receiving 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
Node: h2(1) (root):
# iperf -c 172.16.20.10 -p 5001 -u -b 1M
...
Node: h2(2) (root):
# iperf -c 172.16.20.10 -p 5002 -u -b 300K
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 172.16.20.10, UDP port 5002
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 172.16.10.10 port 44077 connected with 172.16.20.10 port 5002
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.1 sec 369 KBytes 300 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 257 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.2 sec 369 KBytes 295 Kbits/sec 17.379 ms 0/ 257 (0%)
Node: h2(3) (root):
# iperf -c 172.16.20.10 -p 5003 -u -b 600K
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 172.16.20.10, UDP port 5003
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 172.16.10.10 port 59280 connected with 172.16.20.10 port 5003
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec 5.401 ms 0/ 512 (0%)
Node: h1(1) (root):
[ 4] local 172.16.20.10 port 5001 connected with 172.16.10.10 port 37329
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 4] 0.0- 1.0 sec 119 KBytes 976 Kbits/sec 0.639 ms 0/ 83 (0%)
[ 4] 1.0- 2.0 sec 118 KBytes 964 Kbits/sec 0.680 ms 0/ 82 (0%)
[ 4] 2.0- 3.0 sec 87.6 KBytes 717 Kbits/sec 5.817 ms 0/ 61 (0%)
[ 4] 3.0- 4.0 sec 81.8 KBytes 670 Kbits/sec 5.700 ms 0/ 57 (0%)
[ 4] 4.0- 5.0 sec 66.0 KBytes 541 Kbits/sec 12.772 ms 0/ 46 (0%)
[ 4] 5.0- 6.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 60.590 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 6.0- 7.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 89.968 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 7.0- 8.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 108.364 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 8.0- 9.0 sec 10.0 KBytes 82.3 Kbits/sec 125.635 ms 0/ 7 (0%)
[ 4] 9.0-10.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 130.604 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 10.0-11.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 140.192 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 11.0-12.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 144.411 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 12.0-13.0 sec 28.7 KBytes 235 Kbits/sec 63.964 ms 0/ 20 (0%)
[ 4] 13.0-14.0 sec 44.5 KBytes 365 Kbits/sec 26.721 ms 0/ 31 (0%)
[ 4] 14.0-15.0 sec 57.4 KBytes 470 Kbits/sec 9.396 ms 0/ 40 (0%)
[ 4] 15.0-16.0 sec 118 KBytes 964 Kbits/sec 0.956 ms 0/ 82 (0%)
[ 4] 16.0-17.0 sec 119 KBytes 976 Kbits/sec 0.820 ms 0/ 83 (0%)
[ 4] 17.0-18.0 sec 118 KBytes 964 Kbits/sec 0.741 ms 0/ 82 (0%)
[ 4] 18.0-19.0 sec 118 KBytes 964 Kbits/sec 0.839 ms 0/ 82 (0%)
[ 4] 0.0-19.7 sec 1.19 MBytes 508 Kbits/sec 0.981 ms 0/ 852 (0%)
The above result shows the traffic marked with AF41 (sent to the port 5003) is guaranteed 500Kbps bandwidth, and the traffic marked with AF31 (sent to the port 5002) is guaranteed 200Kbps bandwidth. On the other hand, the bandwidth of best-effort traffic is limited while the traffic marked with AF class is communicating.
In this way, we were able to confirm that it is possible to realize a QoS by using DiffServ model.
Example of the operation of QoS by using Meter Table¶
Meter Table is introduced in the OpenFlow 1.3, makes it enable to use policing of traffic in OpenFlow mechanism. This chapter describes example of the use of Meter Table. This example uses the OpenFlow Switch ofsoftswitch13(https://github.com/CPqD/ofsoftswitch13). This switch supports Meter Table.
Note
This section does not describe the installation instructions for ofsoftswitch13.
Reference: https://github.com/CPqD/ofsoftswitch13/wiki/OpenFlow-1.3-Tutorial
The following shows an example of the network composed of the multiple DiffServ domain (DS domain). Traffic metering are executed by the router (edge router) located on the boundary of the DS domain, and the traffic that exceeds the specified bandwidth will be re-marking. Usually, re-marked packets are dropped preferentially or treated as low priority class. In this example, perform the bandwidth guarantee of 800Kbps to AF1 class. Also, AF11 class traffic transferred from each DS domain is guaranteed with 400Kbps bandwidth. Traffic that is more than 400kbps is treated as excess traffic, and re-marked with AF12 class. However, it is still guaranteed that AF12 class is more preferentially transferred than the best effort class.
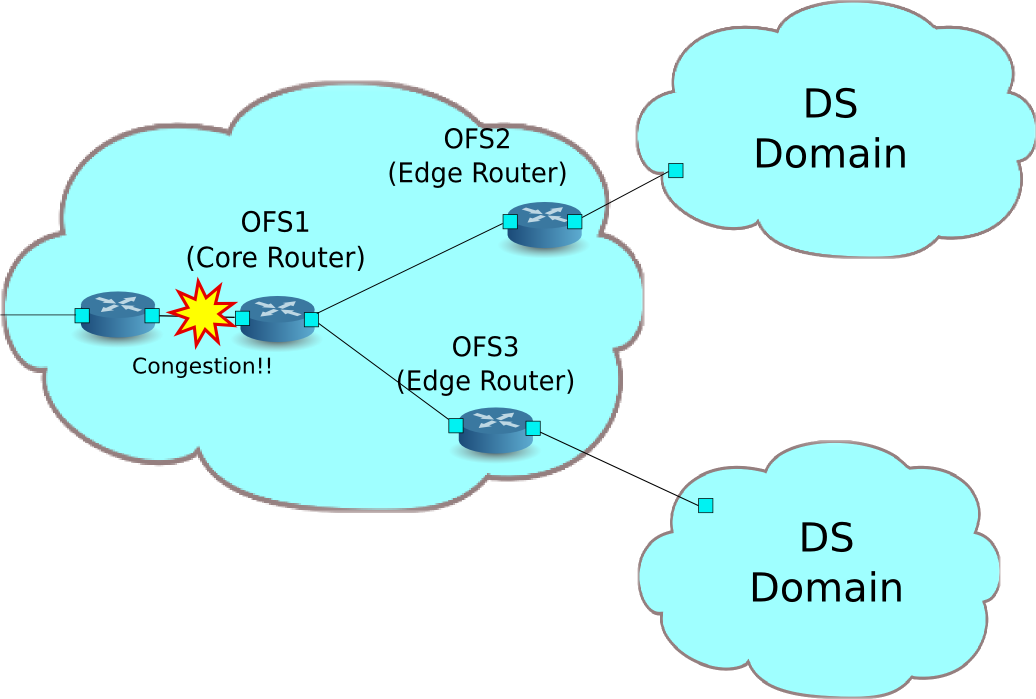
Building the environment¶
First, build an environment on Mininet. Build a topology using a python script.
source code: qos_sample_topology.py
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.topo import Topo
from mininet.node import UserSwitch
from mininet.node import RemoteController
class SliceableSwitch(UserSwitch):
def __init__(self, name, **kwargs):
UserSwitch.__init__(self, name, '', **kwargs)
class MyTopo(Topo):
def __init__( self ):
"Create custom topo."
# Initialize topology
Topo.__init__( self )
# Add hosts and switches
host01 = self.addHost('h1')
host02 = self.addHost('h2')
host03 = self.addHost('h3')
switch01 = self.addSwitch('s1')
switch02 = self.addSwitch('s2')
switch03 = self.addSwitch('s3')
# Add links
self.addLink(host01, switch01)
self.addLink(host02, switch02)
self.addLink(host03, switch03)
self.addLink(switch01, switch02)
self.addLink(switch01, switch03)
def run(net):
s1 = net.getNodeByName('s1')
s1.cmdPrint('dpctl unix:/tmp/s1 queue-mod 1 1 80')
s1.cmdPrint('dpctl unix:/tmp/s1 queue-mod 1 2 120')
s1.cmdPrint('dpctl unix:/tmp/s1 queue-mod 1 3 800')
def genericTest(topo):
net = Mininet(topo=topo, switch=SliceableSwitch,
controller=RemoteController)
net.start()
run(net)
CLI(net)
net.stop()
def main():
topo = MyTopo()
genericTest(topo)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Note
Change the link speed of ofsoftswitch13 to 1Mbps in advance.
First, modify the sourcecode of ofsoftswitch13.
$ cd ofsoftswitch13
$ gedit lib/netdev.c
lib/netdev.c:
644 if (ecmd.autoneg) {
645 netdev->curr |= OFPPF_AUTONEG;
646 }
647
648 - netdev->speed = ecmd.speed;
649 + netdev->speed = 1; /* Fix to 1Mbps link */
650
651 } else {
652 VLOG_DBG(LOG_MODULE, "ioctl(SIOCETHTOOL) failed: %s", strerror(errno));
653 }
Then, re-install ofsoftswitch13.
$ make clean
$ ./boot.sh
$ ./configure
$ make
$ sudo make install
An execution example is as follows.
$ curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/osrg/ryu-book/master/sources/qos_sample_topology.py
$ sudo python ./qos_sample_topology.py
Unable to contact the remote controller at 127.0.0.1:6633
mininet>
Also, start two xterm for the controller.
mininet> xterm c0
mininet> xterm c0
mininet>
Next, modify the simple_switch_13.py used in “Switching Hub”. rest_qos.py suppose to be processed on Flow Table pipeline processing,modify simple_switch_13.py to register flow entry into table id:1.
controller: c0 (root)
# sed '/OFPFlowMod(/,/)/s/)/, table_id=1)/' ryu/ryu/app/simple_switch_13.py > ryu/ryu/app/qos_simple_switch_13.py
# cd ryu/; python ./setup.py install
Finally, start rest_qos and qos_simple_switch_13 on xterm of controller.
controller: c0 (root):
# ryu-manager ryu.app.rest_qos ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13
loading app ryu.app.rest_qos
loading app ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
instantiating app None of DPSet
creating context dpset
instantiating app None of ConfSwitchSet
creating context conf_switch
creating context wsgi
instantiating app ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13 of SimpleSwitch13
instantiating app ryu.controller.ofp_handler of OFPHandler
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_qos of RestQoSAPI
(2348) wsgi starting up on http://0.0.0.0:8080/
After a successful connection between the switch and Ryu, the following message appears.
controller: c0 (root):
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000003: Join qos switch.
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000001: Join qos switch.
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000002: Join qos switch.
...
Setting QoS¶
Install the following flow entry in accordance with DSCP value into the router (s1).
| (Priority) | DSCP | Queue ID | (QoS ID) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 (BE) | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 12(AF12) | 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 10(AF11) | 3 | 3 |
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "0", "in_port": "2"}, "actions":{"queue": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "10", "in_port": "2"}, "actions":{"queue": "3"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=2"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "12", "in_port": "2"}, "actions":{"queue": "2"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=3"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "0", "in_port": "3"}, "actions":{"queue": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=4"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "10", "in_port": "3"}, "actions":{"queue": "3"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=5"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "12", "in_port": "3"}, "actions":{"queue": "2"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=6"
}
]
}
]
Install the following meter entries to the switches (s2, s3).
| (Priority) | DSCP | Meter ID | (QoS ID) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10(AF11) | 1 | 1 | |
| Meter ID | Flags | Bands |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | KBPS | type:DSCP_REMARK, rate:400000, prec_level:1 |
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "10"}, "actions":{"meter": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"meter_id": "1", "flags": "KBPS", "bands":[{"type":"DSCP_REMARK", "rate": "400", "prec_level": "1"}]}' http://localhost:8080/qos/meter/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Meter added. : Meter ID=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "10"}, "actions":{"meter": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000003
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000003",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"meter_id": "1", "flags": "KBPS", "bands":[{"type":"DSCP_REMARK", "rate": "400", "prec_level": "1"}]}' http://localhost:8080/qos/meter/0000000000000003
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000003",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Meter added. : Meter ID=1"
}
]
}
]
Verifying the Setting¶
Check the contents of the setting of each switch.
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "1"
}
],
"in_port": 2,
"qos_id": 1
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "3"
}
],
"qos_id": 2,
"in_port": 2,
"ip_dscp": 10
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "2"
}
],
"qos_id": 3,
"in_port": 2,
"ip_dscp": 12
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "1"
}
],
"in_port": 3,
"qos_id": 4
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "3"
}
],
"qos_id": 5,
"in_port": 3,
"ip_dscp": 10
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "2"
}
],
"qos_id": 6,
"in_port": 3,
"ip_dscp": 12
}
]
}
]
}
]
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"ip_dscp": 10,
"actions": [
{
"meter": "1"
}
],
"qos_id": 1
}
]
}
]
}
]
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000003
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000003",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"ip_dscp": 10,
"actions": [
{
"meter": "1"
}
],
"qos_id": 1
}
]
}
]
}
]
Measuring the bandwidth¶
Try to measure the bandwidth by using iperf. h1(server) is listening on port 5001 and 5002 and port 5003 in the UDP protocol. h2, h3 (client) sends the traffic of each class addressed to h1.
First, start 4 xterm as follows.
mininet> xterm h1
mininet> xterm h2
mininet> xterm h3
mininet> xterm h3
...
Node: h1(1) (root):
# iperf -s -u -p 5001 &
# iperf -s -u -p 5002 &
# iperf -s -u -p 5003 &
...
Best-effort traffic & AF11 excess traffic¶
Node: h2 (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5001 -u -b 800K
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5001
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.3 port 60324 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5001
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 979 KBytes 800 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 682 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-11.9 sec 650 KBytes 449 Kbits/sec 18.458 ms 229/ 682 (34%)
Node: h3(1) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5002 -u -b 600K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5002
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.2 port 53661 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5002
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec 7.497 ms 6/ 512 (1.2%)
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 6 datagrams received out-of-order
The above result shows, even if the traffic of AF11 exceeds the contracted bandwidth 400Kbps, AF11 is more preferentially guaranteed bandwidth than traffic of best effort.
AF11 excess traffic & Best-effort traffic & AF11 non-excess traffic¶
Node: h2 (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5001 -u -b 600K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5001
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.2 port 49358 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5001
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 666 KBytes 544 Kbits/sec 500.361 ms 48/ 512 (9.4%)
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 192 datagrams received out-of-order
Node: h3(1) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5002 -u -b 500K
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5002
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.3 port 42759 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5002
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 613 KBytes 500 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 427 datagrams
[ 4] WARNING: did not receive ack of last datagram after 10 tries.
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-14.0 sec 359 KBytes 210 Kbits/sec 102.479 ms 177/ 427 (41%)
Node: h3(2) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5003 -u -b 400K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5003
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.3 port 35475 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5003
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.1 sec 491 KBytes 400 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 342 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.5 sec 491 KBytes 384 Kbits/sec 15.422 ms 0/ 342 (0%)
The above result shows, traffic within the contracted bandwidth of 400Kbps are not dropped.
AF11 excess traffic & AF11 excess traffic¶
Node: h2 (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5001 -u -b 600K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5001
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.3 port 50761 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5001
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-11.0 sec 673 KBytes 501 Kbits/sec 964.490 ms 43/ 512 (8.4%)
[ 4] 0.0-11.0 sec 95 datagrams received out-of-order
Node: h3(1) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5002 -u -b 600K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5002
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.2 port 53066 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5002
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.6 sec 665 KBytes 515 Kbits/sec 897.126 ms 49/ 512 (9.6%)
[ 4] 0.0-10.6 sec 93 datagrams received out-of-order
The above result shows, two excess traffic are droped in the same rate.
In this section, you learned how to use the QoS REST API with specific examples.
REST API List¶
A list of REST API of rest_qos introduced in this section.
Get queue status¶
| Method | GET |
| URL | /qos/queue/status/{switch} –switch: [ “all” | Switch ID ] |
Get queue configuration¶
| Method | GET |
| URL | /qos/queue/{switch} –switch: [ “all” | Switch ID ] |
| Remarks | It is possible to get only queue configuration after start of the QoS REST API. |
Set queue¶
| Method | POST |
| URL | /qos/queue/{switch} –switch: [ “all” | Switch ID ] |
| Data | port_name:[Port name] type:[linux-htb | linux-hfsc] max_rate:[Bandwidth(bps)] queues:
|
| Remarks | If an action of the given type exists in the current set, overwrite it. This command is compatible with only Open vSwitch. port_name on Data is optional. If you do not specify a port_name, it is set to OFPP_ANY. |
Delete queue¶
| Method | DELETE |
| URL | /qos/queue/{swtich} –switch: [ “all” | Switch ID ] |
| Remarks | Remove the association with QoS record of OVSDB |
Get all of QoS rules¶
| Method | GET |
| URL | /qos/rules/{switch}[/{vlan}] –switch: [ “all” | Switch ID ] –vlan: [ “all” | VLAN ID ] |
| Remarks | VLAN ID on URL is optional. |
Set a QoS rule¶
| Method | POST |
| URL | /qos/rules/{switch}[/{vlan}] –switch: [ “all” | Switch ID ] –vlan: [ “all” | VLAN ID ] |
| Data | priority:[ 0 - 65535 ] match:
|
| Remarks | If successful registration, QoS ID is generated, it will be described in the response. VLAN ID on URL is optional. |
Delete qos rules¶
| Method | DELETE |
| URL | /qos/rules/{switch}[/{vlan}] –switch: [ “all” | Switch ID ] –vlan: [ “all” | VLAN ID ] |
| Data | rule_id:[ “all” | 1 - ... ] |
| Remarks | VLAN ID on URL is optional. |
Get Meter Statistics¶
| Method | GET |
| URL | /qos/meter/{switch} –switch: [ “all” | Switch ID ] |
Set meter table¶
| Method | POST |
| URL | /qos/meter/{switch} |
| Data | meter_id:Meter ID bands:
|
| Remarks | The parameter specified or enabled in the bands is depends on the action and flags. |