QoS¶
本章では、RESTで設定が出来るQoS機能の使用方法について説明します。
QoSについて¶
QoS(Quality of Service)とはネットワーク上でデータの種類に応じた優先順位に従ってデータを転送したり、ある特定の通信の為にネットワーク帯域を予約し、一定の通信速度で通信できるようにする技術です。OpenFlowでは帯域制御によるQoSが実現できます。
フロー単位のQoSの動作例¶
以下のようなトポロジを想定し、スイッチにQueueの設定とルールを追加し適切な帯域幅を割り当てる例を紹介します。また、OFS1のWAN側インターフェースでトラフィックシェーピングを行う場合を想定しています。
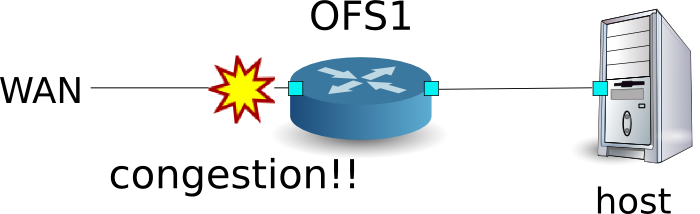
環境構築¶
まずはMininet上に環境を構築します。mnコマンドのパラメータは以下のようになります。
| パラメータ | 値 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|
| mac | なし | 自動的にホストのMACアドレスをセットする |
| switch | ovsk | Open vSwitchを使用する |
| controller | remote | OpenFlowコントローラは外部のものを利用する |
| x | なし | xtermを起動する |
実行例は以下のようになります。
$ sudo mn --mac --switch ovsk --controller remote -x
*** Creating network
*** Adding controller
Unable to contact the remote controller at 127.0.0.1:6633
*** Adding hosts:
h1 h2
*** Adding switches:
s1
*** Adding links:
(h1, s1) (h2, s1)
*** Configuring hosts
h1 h2
*** Running terms on localhost:10.0
*** Starting controller
*** Starting 1 switches
s1
*** Starting CLI:
mininet>
また、コントローラ用のxtermをもうひとつ起動しておきます。
mininet> xterm c0
mininet>
続いて、スイッチで使用するOpenFlowのバージョンを1.3に設定します。また、OVSDBへアクセスを行うため、6632ポートで待ち受けるように設定します。
switch: s1 (root):
# ovs-vsctl set Bridge s1 protocols=OpenFlow13
# ovs-vsctl set-manager ptcp:6632
続いて、「スイッチングハブ」で使用したsimple_switch_13.pyを変更します。rest_qos.pyはフローテーブルのパイプライン上で処理される事を想定しているため、simple_switch_13.pyのフローエントリをtable id:1に登録するように変更します。
controller: c0 (root)
# sed '/OFPFlowMod(/,/)/s/)/, table_id=1)/' ryu/ryu/app/simple_switch_13.py > ryu/ryu/app/qos_simple_switch_13.py
# cd ryu/; python ./setup.py install
最後に、コントローラのxterm上でrest_qos、qos_simple_switch_13、rest_conf_switchを起動させます。
controller: c0 (root):
# ryu-manager ryu.app.rest_qos ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13 ryu.app.rest_conf_switch
loading app ryu.app.rest_qos
loading app ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13
loading app ryu.app.rest_conf_switch
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
instantiating app None of DPSet
creating context dpset
instantiating app None of ConfSwitchSet
creating context conf_switch
creating context wsgi
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_conf_switch of ConfSwitchAPI
instantiating app ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13 of SimpleSwitch13
instantiating app ryu.controller.ofp_handler of OFPHandler
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_qos of RestQoSAPI
(3519) wsgi starting up on http://0.0.0.0:8080/
Ryuとスイッチの間の接続に成功すると、次のメッセージが表示されます。
controller: c0 (root):
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000001: Join qos switch.
上記ログが表示されれば、準備完了です。
Queueの設定¶
スイッチにQueueを設定します。
| キューID | 最大レート | 最小レート |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 500Kbps | - |
| 1 | (1Mbps) | 800Kbps |
注釈
以降の説明で使用するREST APIの詳細は、章末の「REST API一覧」を参照してください。
まずは、OVSDBへアクセスする為の設定を行います。
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X PUT -d '"tcp:127.0.0.1:6632"' http://localhost:8080/v1.0/conf/switches/0000000000000001/ovsdb_addr
#
続いて、Queueの設定を行います。
# curl -X POST -d '{"port_name": "s1-eth1", "type": "linux-htb", "max_rate": "1000000", "queues": [{"max_rate": "500000"}, {"min_rate": "800000"}]}' http://localhost:8080/qos/queue/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": {
"result": "success",
"details": {
"0": {
"config": {
"max-rate": "500000"
}
},
"1": {
"config": {
"min-rate": "800000"
}
}
}
}
}
]
注釈
RESTコマンドの実行結果は見やすいように整形しています。
QoSの設定¶
以下の通りスイッチにフローの設定を行います。
| (優先度) | 宛先 | 宛先ポート | プロトコル | Queue ID | (QoS ID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.0.0.1 | 5002 | UDP | 1 | 1 |
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"nw_dst": "10.0.0.1", "nw_proto": "UDP", "tp_dst": "5002"}, "actions":{"queue": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
設定内容の確認¶
各スイッチに設定された内容を確認します。
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"nw_proto": "UDP",
"tp_dst": 5002,
"qos_id": 1,
"nw_dst": "10.0.0.1",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "1"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
]
帯域計測¶
この状態で、iperfで帯域計測をしてみます。h1はサーバとなりプロトコルはUDPで5001ポートと5002ポートで待ち受けます。h2はクライアントとなりh1の5001ポートに1MbpsのUDPトラフィック、h1の5002ポートに1MbpsのUDPトラフィックを送出します。
注釈
以降の例では、帯域計測にiperf(http://iperf.fr/)を使用します。iperfのインストール、使用方法については、本稿では解説しません。
まず、h1、h2のターミナルを一つずつ起動します。
mininet> xterm h1
mininet> xterm h2
Node: h1(1) (root):
# iperf -s -u -i 1 -p 5001
...
Node: h1(2) (root):
# iperf -s -u -i 1 -p 5002
...
Node: h2(1) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5001 -u -b 1M
...
Node: h2(2) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5002 -u -b 1M
...
Node: h1(1) (root):
[ 4] local 10.0.0.1 port 5001 connected with 10.0.0.2 port 50375
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 4] 0.0- 1.0 sec 60.3 KBytes 494 Kbits/sec 12.208 ms 4/ 42 (9.5%)
[ 4] 0.0- 1.0 sec 4 datagrams received out-of-order
[ 4] 1.0- 2.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.538 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 2.0- 3.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.494 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 3.0- 4.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.625 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 4.0- 5.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.576 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 5.0- 6.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.561 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 6.0- 7.0 sec 11.5 KBytes 94.1 Kbits/sec 45.536 ms 0/ 8 (0%)
[ 4] 7.0- 8.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 92.790 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 8.0- 9.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 135.391 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 9.0-10.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 167.045 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 10.0-11.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 193.006 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 11.0-12.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 213.944 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 12.0-13.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 231.981 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 13.0-14.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 249.758 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 14.0-15.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 261.139 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 15.0-16.0 sec 4.31 KBytes 35.3 Kbits/sec 269.879 ms 0/ 3 (0%)
[ 4] 16.0-17.0 sec 12.9 KBytes 106 Kbits/sec 204.755 ms 0/ 9 (0%)
[ 4] 17.0-18.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 26.214 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 18.0-19.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 13.485 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 19.0-20.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.690 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 20.0-21.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.498 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 21.0-22.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.601 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 22.0-23.0 sec 60.3 KBytes 494 Kbits/sec 12.640 ms 0/ 42 (0%)
[ 4] 23.0-24.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.508 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 24.0-25.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.578 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 25.0-26.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.541 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 26.0-27.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.539 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 27.0-28.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.578 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 28.0-29.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.527 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 29.0-30.0 sec 58.9 KBytes 482 Kbits/sec 12.542 ms 0/ 41 (0%)
[ 4] 0.0-30.6 sec 1.19 MBytes 327 Kbits/sec 12.562 ms 4/ 852 (0.47%)
[ 4] 0.0-30.6 sec 4 datagrams received out-of-order
Node: h1(2) (root):
[ 4] local 10.0.0.1 port 5002 connected with 10.0.0.2 port 60868
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 4] 0.0- 1.0 sec 112 KBytes 917 Kbits/sec 4.288 ms 0/ 78 (0%)
[ 4] 1.0- 2.0 sec 115 KBytes 941 Kbits/sec 4.168 ms 0/ 80 (0%)
[ 4] 2.0- 3.0 sec 115 KBytes 941 Kbits/sec 4.454 ms 0/ 80 (0%)
[ 4] 3.0- 4.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.226 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 4.0- 5.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.096 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 5.0- 6.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.225 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 6.0- 7.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.055 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 7.0- 8.0 sec 113 KBytes 929 Kbits/sec 4.241 ms 0/ 79 (0%)
[ 4] 8.0- 9.0 sec 115 KBytes 941 Kbits/sec 3.886 ms 0/ 80 (0%)
[ 4] 9.0-10.0 sec 112 KBytes 917 Kbits/sec 3.969 ms 0/ 78 (0%)
[ 4] 0.0-10.8 sec 1.19 MBytes 931 Kbits/sec 4.287 ms 0/ 852 (0%)
結果から分かる通りに5001ポート宛のトラフィックは帯域制限により500Kbps以下にシェーピングされ、5002ポート宛のトラフィックは800kbpsの帯域保証が行われていることが分かります。
DiffServによるQoSの動作例¶
先ほどの例ではフロー毎にQoSを行いましたが、きめ細かい制御ができる反面、扱うフローが増加するに伴い、帯域制御を行う各スイッチに設定するフローも増加し、スケーラブルではありません。そこでフロー毎にQoSを行うのではなく、DiffServドメインの入り口のルータでフローをいくつかのクラスに分け、クラス毎の制御を行うDiffServを適用します。DiffServではIPヘッダのToSフィールド内の6ビットのDSCP値を使用し、DSCP値により定義されるPHBに従って転送することで、QoSを実現します。
以下のようなトポロジを想定し、スイッチ(ルータ)OFS1にQueueの設定とクラスに応じた帯域制御を設定し、ルータOFS2にはフローに応じたDSCP値をマーキングを行うルールを適用する例を紹介します。また、OFS1のWAN側インターフェースでトラフィックシェーピングを行う場合を想定しています。
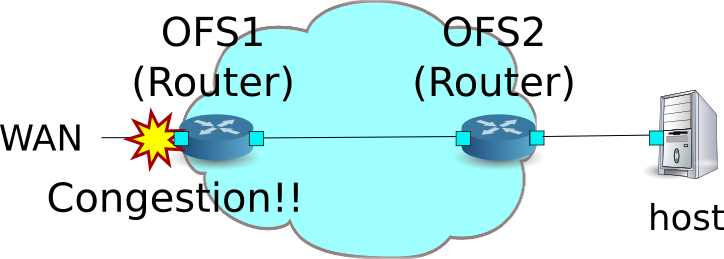
環境構築¶
まずはMininet上に環境を構築します。mnコマンドのパラメータは以下のようになります。
| パラメータ | 値 | 説明 |
|---|---|---|
| topo | linear,2 | 2台のスイッチが直列に接続されているトポロジ |
| mac | なし | 自動的にホストのMACアドレスをセットする |
| switch | ovsk | Open vSwitchを使用する |
| controller | remote | OpenFlowコントローラは外部のものを利用する |
| x | なし | xtermを起動する |
実行例は以下のようになります。
$ sudo mn --topo linear,2 --mac --switch ovsk --controller remote -x
*** Creating network
*** Adding controller
Unable to contact the remote controller at 127.0.0.1:6633
*** Adding hosts:
h1 h2
*** Adding switches:
s1
*** Adding links:
(h1, s1) (h2, s1)
*** Configuring hosts
h1 h2
*** Running terms on localhost:10.0
*** Starting controller
*** Starting 1 switches
s1
*** Starting CLI:
mininet>
また、コントローラ用のxtermをもうひとつ起動しておきます。
mininet> xterm c0
mininet>
続いて、スイッチで使用するOpenFlowのバージョンを1.3に設定します。また、OVSDBへアクセスを行うため、6632ポートで待ち受けるように設定します。
switch: s1 (root):
# ovs-vsctl set Bridge s1 protocols=OpenFlow13
# ovs-vsctl set-manager ptcp:6632
switch: s2 (root):
# ovs-vsctl set Bridge s2 protocols=OpenFlow13
その後、各ホストで自動的に割り当てられているIPアドレスを削除し、新たにIPアドレスを設定します。
host: h1:
# ip addr del 10.0.0.1/8 dev h1-eth0
# ip addr add 172.16.20.10/24 dev h1-eth0
host: h2:
# ip addr del 10.0.0.2/8 dev h2-eth0
# ip addr add 172.16.10.10/24 dev h2-eth0
続いて、「ルータ」で使用したrest_router.pyを変更します。rest_qos.pyはフローテーブルのパイプライン上で処理される事を想定しているため、rest_router.pyのフローエントリをtable id:1に登録するように変更します。
controller: c0 (root):
# sed '/OFPFlowMod(/,/)/s/0, cmd/1, cmd/' ryu/ryu/app/rest_router.py > ryu/ryu/app/qos_rest_router.py
# cd ryu/; python ./setup.py install
最後に、コントローラのxterm上でrest_qos、qos_rest_router、rest_conf_switchを起動させます。
controller: c0 (root):
# ryu-manager ryu.app.rest_qos ryu.app.qos_rest_router ryu.app.rest_conf_switch
loading app ryu.app.rest_qos
loading app ryu.app.qos_rest_router
loading app ryu.app.rest_conf_switch
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
instantiating app None of DPSet
creating context dpset
instantiating app None of ConfSwitchSet
creating context conf_switch
creating context wsgi
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_conf_switch of ConfSwitchAPI
instantiating app ryu.app.qos_rest_router of RestRouterAPI
instantiating app ryu.controller.ofp_handler of OFPHandler
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_qos of RestQoSAPI
(4687) wsgi starting up on http://0.0.0.0:8080/
Ryuとスイッチの間の接続に成功すると、次のメッセージが表示されます。
controller: c0 (root):
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Set SW config for TTL error packet in.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Set ARP handling (packet in) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Set L2 switching (normal) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Set default route (drop) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Start cyclic routing table update.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000002: Join as router.
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000002: Join qos switch.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Set SW config for TTL error packet in.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Set ARP handling (packet in) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Set L2 switching (normal) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Set default route (drop) flow [cookie=0x0]
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Start cyclic routing table update.
[RT][INFO] switch_id=0000000000000001: Join as router.
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000001: Join qos switch.
上記ログが表示されれば、準備完了です。
Queueの設定¶
| キューID | 最大レート | 最小レート | クラス |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1Mbps | - | Default |
| 1 | (1Mbps) | 200Kbps | AF3 |
| 2 | (1Mbps) | 500Kbps | AF4 |
注釈
以降の説明で使用するREST APIの詳細は、章末の「REST API一覧」を参照してください。
まずは、OVSDBへアクセスする為の設定を行います。
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X PUT -d '"tcp:127.0.0.1:6632"' http://localhost:8080/v1.0/conf/switches/0000000000000001/ovsdb_addr
#
続いて、Queueの設定を行います。
# curl -X POST -d '{"port_name": "s1-eth1", "type": "linux-htb", "max_rate": "1000000", "queues":[{"max_rate": "1000000"}, {"min_rate": "200000"}, {"min_rate": "500000"}]}' http://localhost:8080/qos/queue/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": {
"result": "success",
"details": {
"0": {
"config": {
"max-rate": "1000000"
}
},
"1": {
"config": {
"min-rate": "200000"
}
},
"2": {
"config": {
"min-rate": "500000"
}
}
}
}
}
]
注釈
RESTコマンドの実行結果は見やすいように整形しています。
ルータの設定¶
各ルータへアドレスの設定、デフォルトルートの設定を行います。
# curl -X POST -d '{"address": "172.16.20.1/24"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add address [address_id=1]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"address": "172.16.30.10/24"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add address [address_id=2]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"gateway": "172.16.30.1"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add route [route_id=1]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"address": "172.16.10.1/24"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add address [address_id=1]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"address": "172.16.30.1/24"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add address [address_id=2]"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"gateway": "172.16.30.10"}' http://localhost:8080/router/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Add route [route_id=1]"
}
]
}
]
...
ルータへのIPアドレスの設定ができたので、各ホストにデフォルトゲートウェイとして登録します。
host: h1:
# ip route add default via 172.16.20.1
host: h2:
# ip route add default via 172.16.10.1
QoSの設定¶
以下の通りルータ(s1)にDSCP値に応じた制御を行うフローを設定します。
| (優先度) | DSCP | キューID | (QoS ID) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26(AF31) | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 34(AF41) | 2 | 2 |
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "26"}, "actions":{"queue": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "34"}, "actions":{"queue": "2"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=2"
}
]
}
]
以下の通りルータ(s2)にマーキングを行うフローの設定を行います。
| (優先度) | 宛先 | 宛先ポート | プロトコル | DSCP | (QoS ID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 172.16.20.10 | 5002 | UDP | 26(AF31) | 1 |
| 1 | 172.16.20.10 | 5003 | UDP | 34(AF41) | 2 |
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"nw_dst": "172.16.20.10", "nw_proto": "UDP", "tp_dst": "5002"}, "actions":{"mark": "26"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"nw_dst": "172.16.20.10", "nw_proto": "UDP", "tp_dst": "5003"}, "actions":{"mark": "34"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=2"
}
]
}
]
設定内容の確認¶
各スイッチに設定された内容を確認します。
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"ip_dscp": 34,
"actions": [
{
"queue": "2"
}
],
"qos_id": 2
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"ip_dscp": 26,
"actions": [
{
"queue": "1"
}
],
"qos_id": 1
}
]
}
]
}
]
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"nw_proto": "UDP",
"tp_dst": 5002,
"qos_id": 1,
"nw_dst": "172.16.20.10",
"actions": [
{
"mark": "26"
}
]
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"nw_proto": "UDP",
"tp_dst": 5003,
"qos_id": 2,
"nw_dst": "172.16.20.10",
"actions": [
{
"mark": "34"
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
]
帯域計測¶
この状態で、iperfで帯域計測をしてみます。h1はサーバとなりプロトコルはUDPで5001ポートと5002ポートと5003ポートで待ち受けます。h2はクライアントとなりh1の5001ポートに1MbpsのUDPトラフィック、h1の5002ポートに300KbpsのUDPトラフィック、h1の5003ポートに600KbpsのUDPトラフィックを送出します。
まず、h2のターミナルを2つ起動します。
mininet> xterm h2
mininet> xterm h2
Node: h1(1) (root):
# iperf -s -u -p 5002 &
...
# iperf -s -u -p 5003 &
...
# iperf -s -u -i 1 5001
------------------------------------------------------------
Server listening on UDP port 5001
Receiving 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
Node: h2(1) (root):
# iperf -c 172.16.20.10 -p 5001 -u -b 1M
...
Node: h2(2) (root):
# iperf -c 172.16.20.10 -p 5002 -u -b 300K
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 172.16.20.10, UDP port 5002
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 172.16.10.10 port 44077 connected with 172.16.20.10 port 5002
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.1 sec 369 KBytes 300 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 257 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.2 sec 369 KBytes 295 Kbits/sec 17.379 ms 0/ 257 (0%)
Node: h2(3) (root):
# iperf -c 172.16.20.10 -p 5003 -u -b 600K
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 172.16.20.10, UDP port 5003
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 172.16.10.10 port 59280 connected with 172.16.20.10 port 5003
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec 5.401 ms 0/ 512 (0%)
Node: h1(1) (root):
[ 4] local 172.16.20.10 port 5001 connected with 172.16.10.10 port 37329
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Jitter Lost/Total Datagrams
[ 4] 0.0- 1.0 sec 119 KBytes 976 Kbits/sec 0.639 ms 0/ 83 (0%)
[ 4] 1.0- 2.0 sec 118 KBytes 964 Kbits/sec 0.680 ms 0/ 82 (0%)
[ 4] 2.0- 3.0 sec 87.6 KBytes 717 Kbits/sec 5.817 ms 0/ 61 (0%)
[ 4] 3.0- 4.0 sec 81.8 KBytes 670 Kbits/sec 5.700 ms 0/ 57 (0%)
[ 4] 4.0- 5.0 sec 66.0 KBytes 541 Kbits/sec 12.772 ms 0/ 46 (0%)
[ 4] 5.0- 6.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 60.590 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 6.0- 7.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 89.968 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 7.0- 8.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 108.364 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 8.0- 9.0 sec 10.0 KBytes 82.3 Kbits/sec 125.635 ms 0/ 7 (0%)
[ 4] 9.0-10.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 130.604 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 10.0-11.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 140.192 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 11.0-12.0 sec 8.61 KBytes 70.6 Kbits/sec 144.411 ms 0/ 6 (0%)
[ 4] 12.0-13.0 sec 28.7 KBytes 235 Kbits/sec 63.964 ms 0/ 20 (0%)
[ 4] 13.0-14.0 sec 44.5 KBytes 365 Kbits/sec 26.721 ms 0/ 31 (0%)
[ 4] 14.0-15.0 sec 57.4 KBytes 470 Kbits/sec 9.396 ms 0/ 40 (0%)
[ 4] 15.0-16.0 sec 118 KBytes 964 Kbits/sec 0.956 ms 0/ 82 (0%)
[ 4] 16.0-17.0 sec 119 KBytes 976 Kbits/sec 0.820 ms 0/ 83 (0%)
[ 4] 17.0-18.0 sec 118 KBytes 964 Kbits/sec 0.741 ms 0/ 82 (0%)
[ 4] 18.0-19.0 sec 118 KBytes 964 Kbits/sec 0.839 ms 0/ 82 (0%)
[ 4] 0.0-19.7 sec 1.19 MBytes 508 Kbits/sec 0.981 ms 0/ 852 (0%)
AF41にマーキングされているトラフィックは500Kbpsの帯域保証がされ、AF31にマーキングされているトラフィックは200Kbpsの帯域保証がされています。一方、ベストエフォートのトラフィックはAFにマーキングされているトラフィックが流れている間は帯域幅が狭められているのが分かります。このようにDiffServによりQoSを実現できることが確認できました。
Meter Tableを使用したQoSの動作例¶
OpenFlow 1.3よりMeter Tableが導入されOpenFlowでトラフィックのポリシングが可能となりました。Meter Tableの利用例について紹介します。こちらの例では、Meter TableをサポートするOpenFlow Switchのofsoftswitch13(https://github.com/CPqD/ofsoftswitch13)を使用します。
注釈
ofsoftswitch13のインストール手順などについては本稿では解説しません。参考:(https://github.com/CPqD/ofsoftswitch13/wiki/OpenFlow-1.3-Tutorial)
以下のように複数のDiffServドメイン(DSドメイン)により構成されているネットワークを想定します。DSドメインの境界に位置するルータ(エッジルータ)によってメータリングが行われ、指定帯域を超えるトラフィックは再マーキングされます。通常再マーキングされたパケットは優先的に破棄されるか、優先順位の低いクラスとして扱われます。例では、AF1クラスに対して800Kbpsの帯域保証を行い、各DSドメインから流入するAF11のトラフィックの400Kbpsを契約帯域とし、それ以上は超過トラフィックとしてパケットはAF12に再マーキングされます。ただし、AF12はベストエフォートのトラフィックよりは保証されるように設定しています。
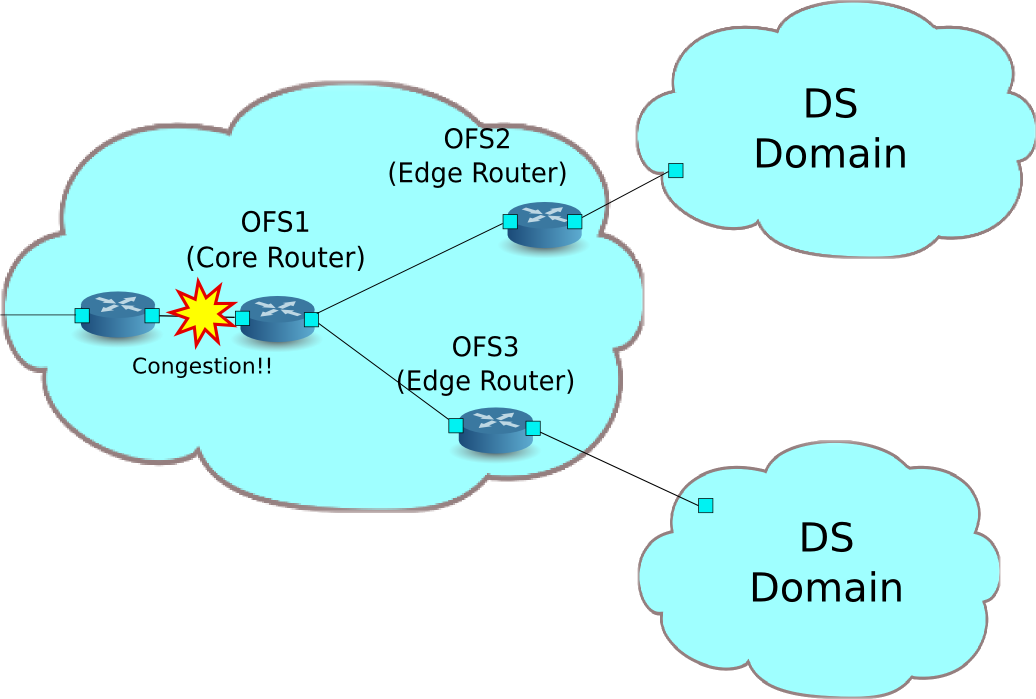
環境構築¶
まずはMininet上に環境を構築します。トポロジの作成はPythonスクリプトで行います。
ソース名:qos_sample_topology.py
from mininet.net import Mininet
from mininet.cli import CLI
from mininet.topo import Topo
from mininet.node import UserSwitch
from mininet.node import RemoteController
class SliceableSwitch(UserSwitch):
def __init__(self, name, **kwargs):
UserSwitch.__init__(self, name, '', **kwargs)
class MyTopo(Topo):
def __init__( self ):
"Create custom topo."
# Initialize topology
Topo.__init__( self )
# Add hosts and switches
host01 = self.addHost('h1')
host02 = self.addHost('h2')
host03 = self.addHost('h3')
switch01 = self.addSwitch('s1')
switch02 = self.addSwitch('s2')
switch03 = self.addSwitch('s3')
# Add links
self.addLink(host01, switch01)
self.addLink(host02, switch02)
self.addLink(host03, switch03)
self.addLink(switch01, switch02)
self.addLink(switch01, switch03)
def run(net):
s1 = net.getNodeByName('s1')
s1.cmdPrint('dpctl unix:/tmp/s1 queue-mod 1 1 80')
s1.cmdPrint('dpctl unix:/tmp/s1 queue-mod 1 2 120')
s1.cmdPrint('dpctl unix:/tmp/s1 queue-mod 1 3 800')
def genericTest(topo):
net = Mininet(topo=topo, switch=SliceableSwitch,
controller=RemoteController)
net.start()
run(net)
CLI(net)
net.stop()
def main():
topo = MyTopo()
genericTest(topo)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
注釈
あらかじめofsoftswitch13のリンクスピードを1Mbpsに変更します。
まず、ofsoftswitch13のソースコードを修正します。
$ cd ofsoftswitch13
$ gedit lib/netdev.c
lib/netdev.c:
644 if (ecmd.autoneg) {
645 netdev->curr |= OFPPF_AUTONEG;
646 }
647
648 - netdev->speed = ecmd.speed;
649 + netdev->speed = 1; /* Fix to 1Mbps link */
650
651 } else {
652 VLOG_DBG(LOG_MODULE, "ioctl(SIOCETHTOOL) failed: %s", strerror(errno));
653 }
そして、ofsoftswitch13を再インストールします。
$ make clean
$ ./boot.sh
$ ./configure
$ make
$ sudo make install
実行例は以下の通りになります
$ curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/osrg/ryu-book/master/sources/qos_sample_topology.py
$ sudo python ./qos_sample_topology.py
Unable to contact the remote controller at 127.0.0.1:6633
mininet>
また、コントローラ用のxtermを2つ起動しておきます。
mininet> xterm c0
mininet> xterm c0
mininet>
続いて、「スイッチングハブ」で使用したsimple_switch_13.pyを変更します。rest_qos.pyはフローテーブルのパイプライン上で処理される事を想定しているため、simple_switch_13.pyのフローエントリをtable id:1に登録するように変更します。
controller: c0 (root)
# sed '/OFPFlowMod(/,/)/s/)/, table_id=1)/' ryu/ryu/app/simple_switch_13.py > ryu/ryu/app/qos_simple_switch_13.py
# cd ryu/; python ./setup.py install
最後に、コントローラのxterm上でrest_qos、qos_simple_switch_13を起動させます。
controller: c0 (root):
# ryu-manager ryu.app.rest_qos ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13
loading app ryu.app.rest_qos
loading app ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
loading app ryu.controller.ofp_handler
instantiating app None of DPSet
creating context dpset
instantiating app None of ConfSwitchSet
creating context conf_switch
creating context wsgi
instantiating app ryu.app.qos_simple_switch_13 of SimpleSwitch13
instantiating app ryu.controller.ofp_handler of OFPHandler
instantiating app ryu.app.rest_qos of RestQoSAPI
(2348) wsgi starting up on http://0.0.0.0:8080/
Ryuとスイッチの間の接続に成功すると、次のメッセージが表示されます。
controller: c0 (root):
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000003: Join qos switch.
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000001: Join qos switch.
[QoS][INFO] dpid=0000000000000002: Join qos switch.
...
QoSの設定¶
以下の通りスイッチ(s1)にDSCP値に応じた制御を行うフローを設定します。
| (優先度) | DSCP | キューID | (QoS ID) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 (BE) | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 12(AF12) | 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 10(AF11) | 3 | 3 |
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "0", "in_port": "2"}, "actions":{"queue": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "10", "in_port": "2"}, "actions":{"queue": "3"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=2"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "12", "in_port": "2"}, "actions":{"queue": "2"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=3"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "0", "in_port": "3"}, "actions":{"queue": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=4"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "10", "in_port": "3"}, "actions":{"queue": "3"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=5"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "12", "in_port": "3"}, "actions":{"queue": "2"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=6"
}
]
}
]
以下の通りスイッチ(s2、s3)にメータエントリーを設定します。
| (優先度) | DSCP | メータID | (QoS ID) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10(AF11) | 1 | 1 |
| メータID | Flags | Bands |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | KBPS | type:DSCP_REMARK,rate:400000,prec_level:1 |
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "10"}, "actions":{"meter": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"meter_id": "1", "flags": "KBPS", "bands":[{"type":"DSCP_REMARK", "rate": "400", "prec_level": "1"}]}' http://localhost:8080/qos/meter/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Meter added. : Meter ID=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"match": {"ip_dscp": "10"}, "actions":{"meter": "1"}}' http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000003
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000003",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "QoS added. : qos_id=1"
}
]
}
]
# curl -X POST -d '{"meter_id": "1", "flags": "KBPS", "bands":[{"type":"DSCP_REMARK", "rate": "400", "prec_level": "1"}]}' http://localhost:8080/qos/meter/0000000000000003
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000003",
"command_result": [
{
"result": "success",
"details": "Meter added. : Meter ID=1"
}
]
}
]
設定内容の確認¶
各スイッチに設定された内容を確認します。
Node: c0 (root):
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000001
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000001",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "1"
}
],
"in_port": 2,
"qos_id": 1
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "3"
}
],
"qos_id": 2,
"in_port": 2,
"ip_dscp": 10
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "2"
}
],
"qos_id": 3,
"in_port": 2,
"ip_dscp": 12
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "1"
}
],
"in_port": 3,
"qos_id": 4
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "3"
}
],
"qos_id": 5,
"in_port": 3,
"ip_dscp": 10
},
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"actions": [
{
"queue": "2"
}
],
"qos_id": 6,
"in_port": 3,
"ip_dscp": 12
}
]
}
]
}
]
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000002
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000002",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"ip_dscp": 10,
"actions": [
{
"meter": "1"
}
],
"qos_id": 1
}
]
}
]
}
]
# curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/qos/rules/0000000000000003
[
{
"switch_id": "0000000000000003",
"command_result": [
{
"qos": [
{
"priority": 1,
"dl_type": "IPv4",
"ip_dscp": 10,
"actions": [
{
"meter": "1"
}
],
"qos_id": 1
}
]
}
]
}
]
帯域計測¶
この状態で、iperfで帯域計測をしてみます。h1はサーバとなりプロトコルはUDPで5001ポートと5002ポートと5003ポートで待ち受けます。h2、h3はクライアントとなりh1宛に各クラスのトラフィックを送出します。
まず、h1とh2で2つとh3の1つづつターミナルを起動します。
mininet> xterm h1
mininet> xterm h2
mininet> xterm h3
mininet> xterm h3
...
Node: h1(1) (root):
# iperf -s -u -p 5001 &
# iperf -s -u -p 5002 &
# iperf -s -u -p 5003 &
...
ベストエフォートと超過したAF11トラフィック¶
Node: h2 (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5001 -u -b 800K
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5001
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.3 port 60324 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5001
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 979 KBytes 800 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 682 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-11.9 sec 650 KBytes 449 Kbits/sec 18.458 ms 229/ 682 (34%)
Node: h3(1) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5002 -u -b 600K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5002
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.2 port 53661 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5002
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec 7.497 ms 6/ 512 (1.2%)
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 6 datagrams received out-of-order
AF11のトラフィックが契約帯域400Kbpsを超過した場合でもベストエフォートのトラフィックより帯域が保証されている事が分かります。
AF11の超過トラフィックとベストエフォートとAF11の契約帯域内トラフィック¶
Node: h2 (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5001 -u -b 600K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5001
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.2 port 49358 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5001
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 666 KBytes 544 Kbits/sec 500.361 ms 48/ 512 (9.4%)
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 192 datagrams received out-of-order
Node: h3(1) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5002 -u -b 500K
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5002
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.3 port 42759 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5002
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 613 KBytes 500 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 427 datagrams
[ 4] WARNING: did not receive ack of last datagram after 10 tries.
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-14.0 sec 359 KBytes 210 Kbits/sec 102.479 ms 177/ 427 (41%)
Node: h3(2) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5003 -u -b 400K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5003
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.3 port 35475 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5003
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.1 sec 491 KBytes 400 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 342 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.5 sec 491 KBytes 384 Kbits/sec 15.422 ms 0/ 342 (0%)
400Kbpsの契約帯域内のトラフィックはドロップされていない事がわかります。
AF11の超過トラフィックとAF11の超過トラフィック¶
Node: h2 (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5001 -u -b 600K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5001
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.3 port 50761 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5001
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-11.0 sec 673 KBytes 501 Kbits/sec 964.490 ms 43/ 512 (8.4%)
[ 4] 0.0-11.0 sec 95 datagrams received out-of-order
Node: h3(1) (root):
# iperf -c 10.0.0.1 -p 5002 -u -b 600K --tos 0x28
------------------------------------------------------------
Client connecting to 10.0.0.1, UDP port 5002
Sending 1470 byte datagrams
UDP buffer size: 208 KByte (default)
------------------------------------------------------------
[ 4] local 10.0.0.2 port 53066 connected with 10.0.0.1 port 5002
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth
[ 4] 0.0-10.0 sec 735 KBytes 600 Kbits/sec
[ 4] Sent 512 datagrams
[ 4] Server Report:
[ 4] 0.0-10.6 sec 665 KBytes 515 Kbits/sec 897.126 ms 49/ 512 (9.6%)
[ 4] 0.0-10.6 sec 93 datagrams received out-of-order
超過トラフィックは同程度にドロップされている事が分かります。
本章では、具体例を挙げながらQoS REST APIの使用方法を説明しました。
REST API一覧¶
本章で紹介したrest_qosのREST API一覧です。
キューの状態の取得¶
| メソッド | GET |
| URL | /qos/queue/status/{switch} –switch: [ “all” |スイッチID] |
キューの設定情報の取得¶
| メソッド | GET |
| URL | /qos/queue/{switch} –switch: [ “all” |スイッチID] |
| 備考 | QoS REST APIを起動した後有効にしたキューの設定情報のみ取得できます。 |
キューの設定¶
| メソッド | POST |
| URL | /qos/queue/{switch} –switch: [ “all” |スイッチID] |
| データ | port_name:[設定対象のポート名] type:[linux-htb | linux-hfsc] max_rate:[帯域幅(bps)] queues:
|
| 備考 | 既存の設定が存在する場合は上書きされます。 OpenvSwitchにのみ設定が可能です。 port_nameパラメータはオプションです。 port_nameを指定しない場合は全てのポートに設定されます。 |
キューの削除¶
| メソッド | DELETE |
| URL | /qos/queue/{swtich} –switch: [ “all” |スイッチID] |
| 備考 | OVSDBのQoSレコードとの関連を削除します。 |
全QoSルールの取得¶
| メソッド | GET |
| URL | /qos/rules/{switch}[/{vlan}] –switch: [ “all” |スイッチID] –vlan: [ “all” |VLAN ID] |
| 備考 | VLAN IDの指定はオプションです。 |
QoSルールの追加¶
| メソッド | POST |
| URL | /qos/rules/{switch}[/{vlan}] –switch: [ “all” |スイッチID] –vlan: [ “all” |VLAN ID] |
| データ | priority:[ 0 - 65535 ] match:
actions:
|
| 備考 | 登録に成功するとQoS IDが生成され、応答に記載されます。 VLAN IDの指定はオプションです。 |
QoSルールの削除¶
| メソッド | DELETE |
| URL | /qos/rules/{switch}[/{vlan}] –switch: [ “all” |スイッチID] –vlan: [ “all” |VLAN ID] |
| データ | rule_id:[ “all” | 1 - ... ] |
| 備考 | VLAN IDの指定はオプションです。 |
メーターテーブルの情報取得¶
| メソッド | GET |
| URL | /qos/meter/{switch} –switch: [ “all” |スイッチID] |
メーターテーブルの設定¶
| メソッド | POST |
| URL | /qos/meter/{switch} |
| データ | meter_id:メータID bands:
|
| 備考 | bandsで指定する、また有効になるパラメータはactionやflagsによって異なります。 |